
Educator Resources
Educators are amazing! To support you and your team on your Tech Challenge adventure, we have compiled some helpful resources.

What do students learn from The Tech Challenge?
Students learn the engineering design process, communication, teamwork, critical thinking and more! The engineering design process is the way engineers approach problem solving. It involves a variety of skills/steps including defining the problem, developing models and using them, investigating, analyzing and interpreting data, applying mathematics and computational thinking, determining solutions, optimizing and looking at trade-offs.
New to The Tech Challenge? Start Here!

Shipwreck Shelters
60 minutes
Build within a time limit using limited materials.
Target timeline: October - December

Engineering Journals
60 minutes
Document ideas, observations, and reflections through diagrams and explanatory text.
Target timeline: October - December

Brainstorming Ideas
Two 60 minute sessions
Develop brainstorming and research skills which can be applied to any problem.
Target timeline: October - December
The Tech Challenge 2025
Build understanding of the science and engineering concepts in the 2025 Tech Challenge with these fun design challenges.
Go Rover Go
165-240 minutes
Design and prototype a device that rolls to a target area.
Target timeline: November - February
New!
Data-Driven Energy Exploration
90 minutes
Explore how to analyze data by building and testing one of three self-powered vehicles. Contribute to a class data set, then iterate on the design based on the data.
Target timeline: November- February
New!
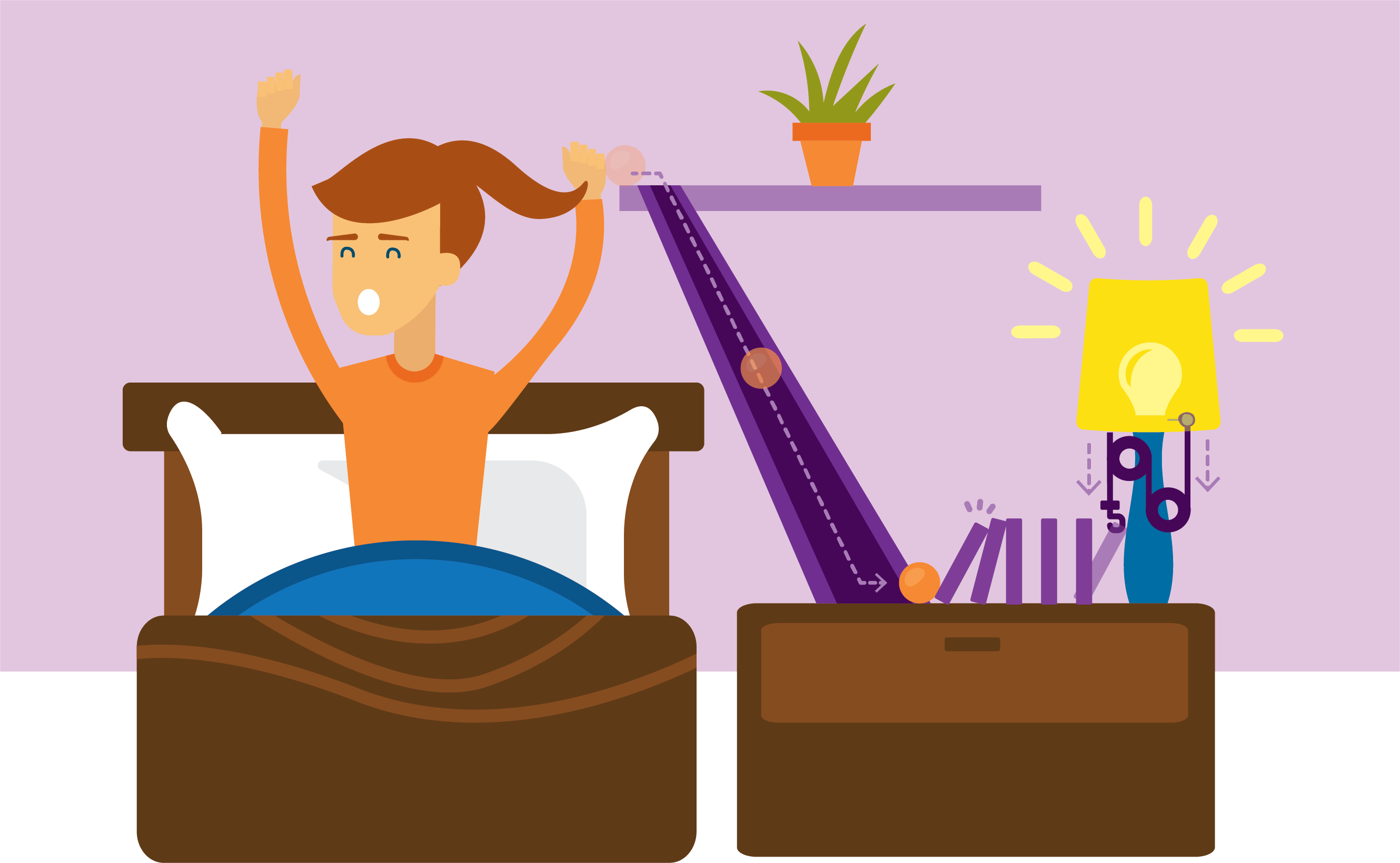

Exploring Chain Reactions
Two 60-minute sessions
Practice building different wheels, axles, pulleys and more!
Target timeline: October - February
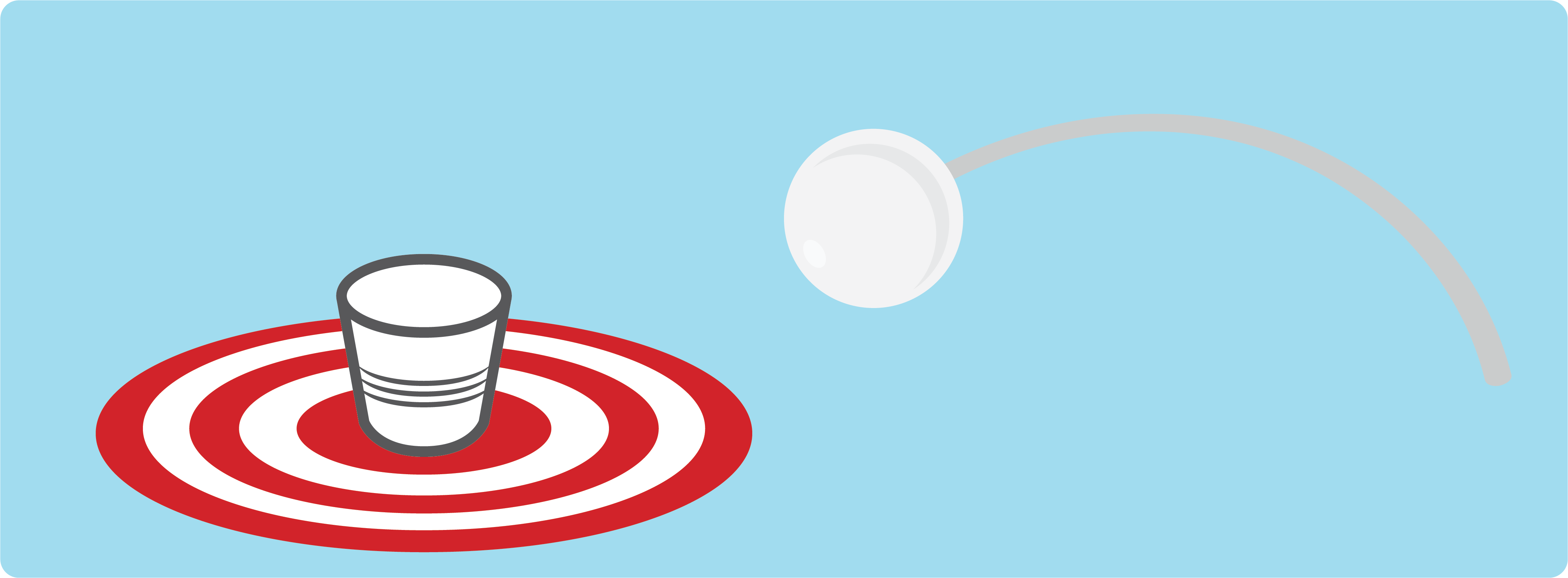

Circle of Pong
60 minutes
Make design considerations based on concepts of potential and kinetic energy.
Target timeline: October - February
Mini Challenges
8 activities
These short engineering challenges are a fun way to practice prototyping.
Target timeline: Any time!
Practice for the Showcase
Use these resources to build confidence and communication skills as you prepare for The Tech Challenge Showcase.
Intergalactic Interview
Two 60-minute sessions
Make design considerations based on concepts of potential and kinetic energy.
Target timeline: March - April

Sharing Tech Tip
Create a classroom culture that supports communication, constructive feedback, and iteration.
Other lessons that can be used with this year’s Tech Challenge
Shipwreck Shelters
Work in teams to build structures that can withstand a natural hazard. Visit three “islands” (stations) and build a structure with only two or three materials.
Engineering Journals
Practice writing and documentation skills, whether in-person or virtual, with this journaling lesson.
Brainstorming Ideas
Teams brainstorm and conceptualize a device that expands.
Count the Seconds
Design a device that can track a specific amount of time and indicate when that time has passed with a sound or visual signal.
Circle of Pong
Students use their knowledge of energy and forces to place a ball in the center of a 6 foot diameter circle.
Standards
The Tech Challenge aligns with the engineering design standards.
Here’s a shortened version of those standards, along with their corresponding sections, for quick reference:
21st Century Skills
The Tech Challenge helps students build 21st century skills such as critical thinking, communication and teamwork. To learn more about 21st century skills, click here.
Vocabulary
Past Tech Challenge Lessons
Click here for past Tech Challenge lessons.

Past Tech Challenge Lessons
Browse resources from previous Tech Challenges.
Adviser Information
For more adviser information, check this out!
 Skip Navigation
Skip Navigation

